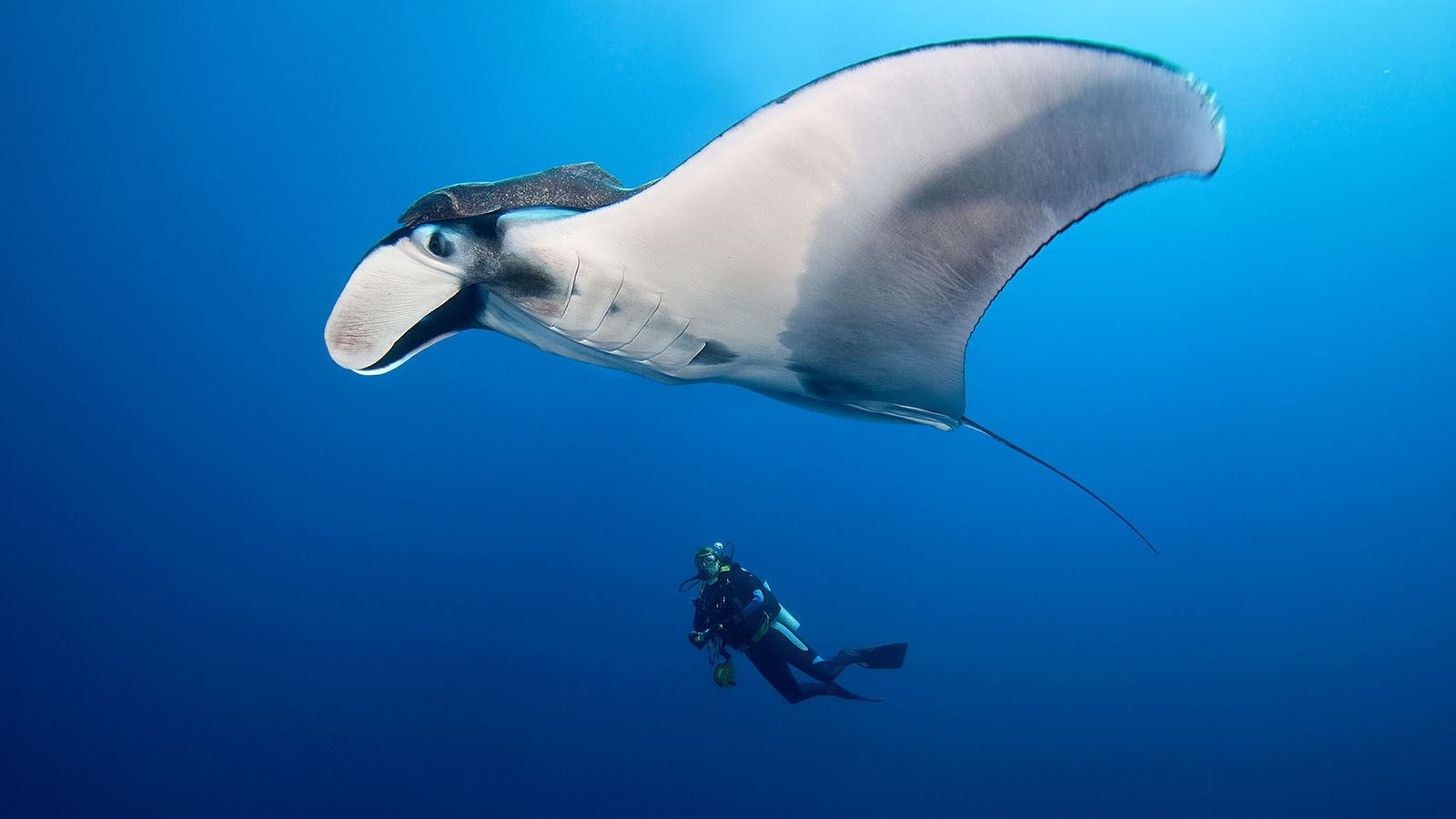






 The giant manta ray is found worldwide in tropical, subtropical, and temperate bodies of water and is commonly found offshore, in oceanic waters, and in productive coastal areas |
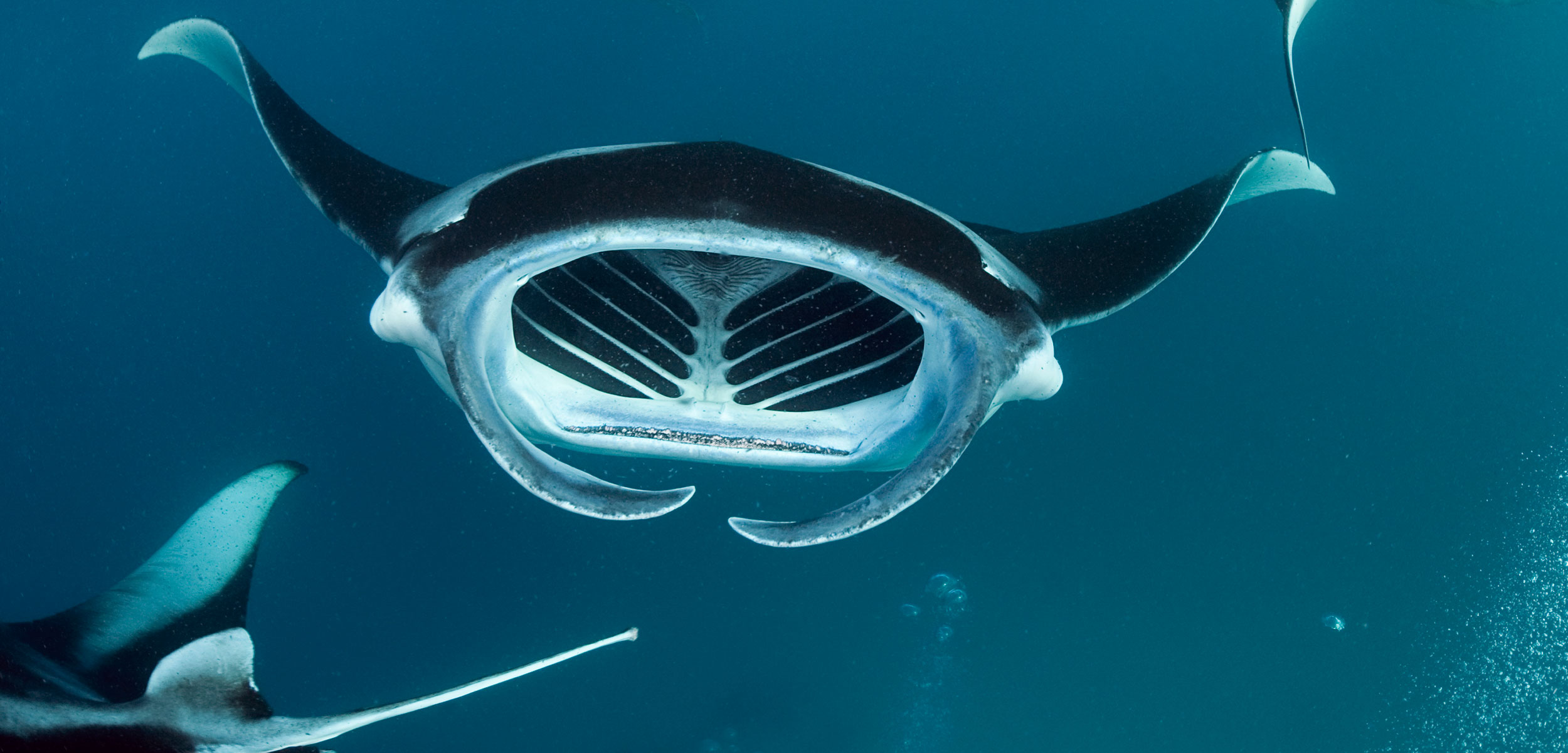
 Manta rays primarily feed on planktonic organisms such as euphausiids, copepods, mysids, decapod larvae, and shrimp |

|
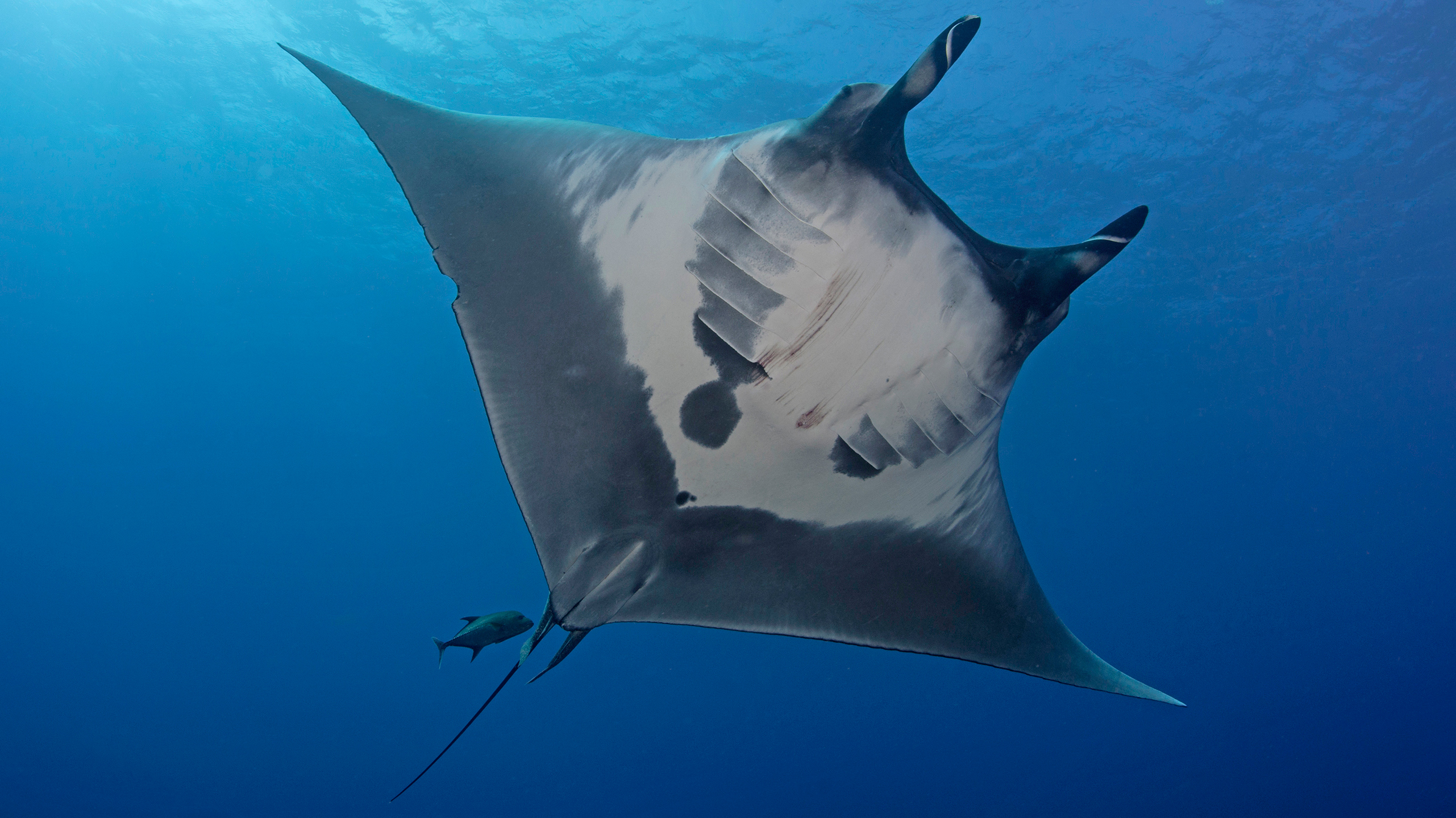
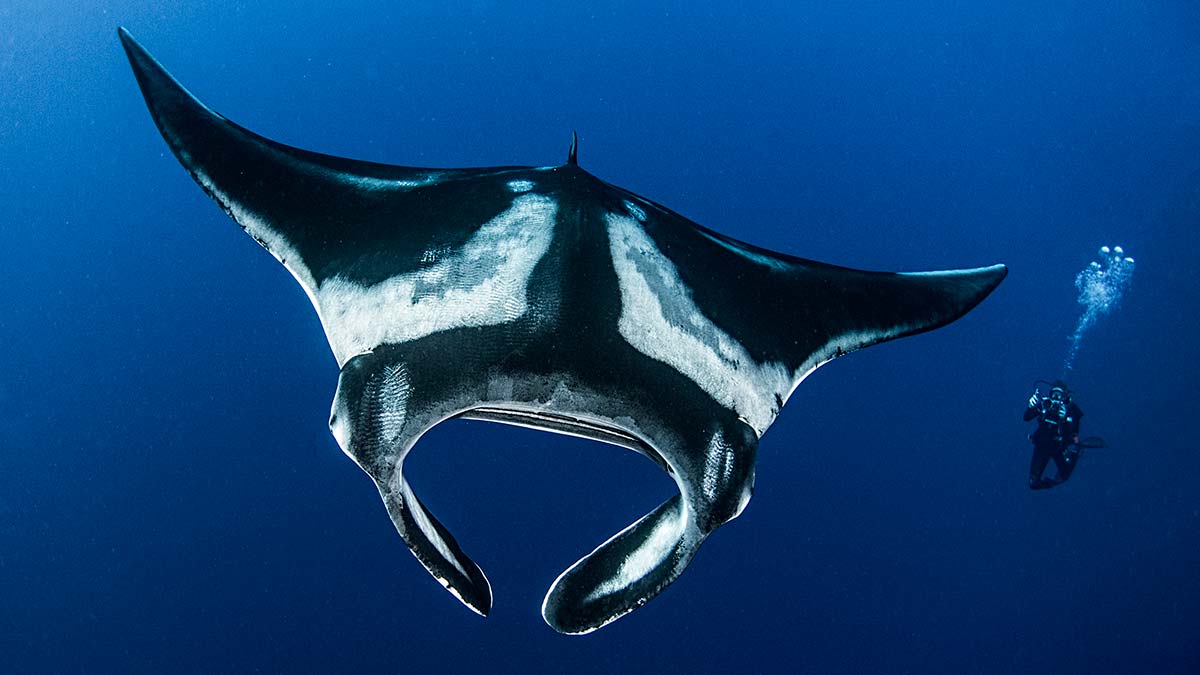
The giant oceanic manta ray can grow to a disc size of up to 7 m (23 ft) across with a weight of about 3,000 kg (6,600 lb) but average size commonly observed is 4.5 m (15 ft).
The largest member of the ray family is the Atlantic manta ray (Mobula birostris), which has an average wingspan of 5.2-6.8 m (17-22 ft). The largest manta ray wingspan ever recorded is 9.1 m (30 ft).
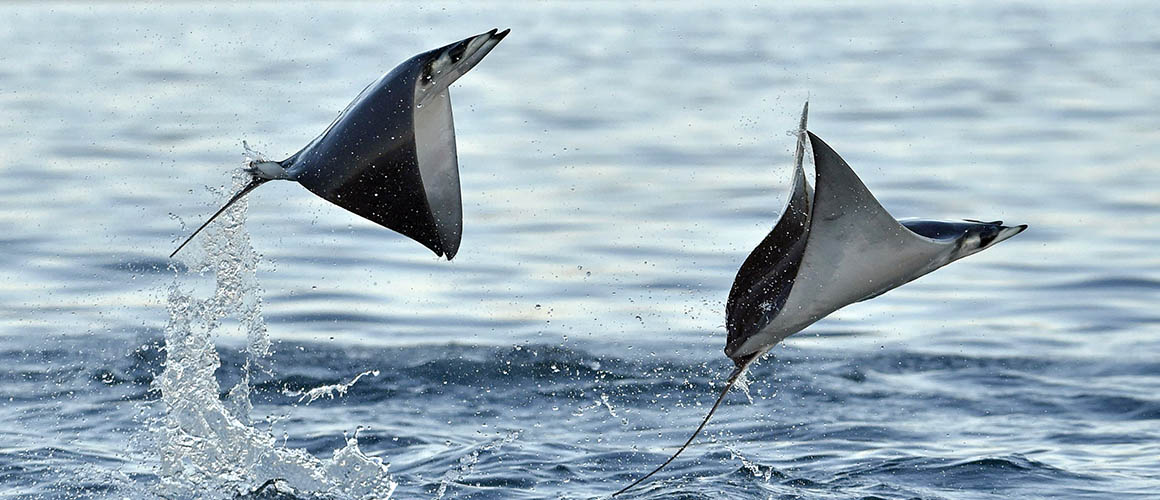
These jumps above the water, known as breaches, come in a number of forms. Sometimes they jump in a perfect arc, entering the water face first. Other times they twist and reenter the water tail first. They have also been known to perform full somersaults in the air! Mantas are well known for their ability to leap above the water, which must have been terrifying for fishermen that were afraid of them! Scientists have a few theories as to why they perform these aerial acrobatics,
Sailors originally viewed manta rays as competition for fish. In reality, these creatures only eat tiny organisms. They are filter feeders that take in large mouthfuls of water and filter out the tiny food particles. These two species are the only members of the ray family that have evolved a filter feeding behavior.